Automating Infrastructure at Scale
Contents
Introduction
In modern IT environments, speed, consistency, and security are crucial. Manual server configuration is slow and error-prone, especially when managing hundreds or thousands of machines. Puppet provides a way to automate these tasks, ensuring infrastructure is configured, deployed, and maintained reliably.
Puppet is widely used by DevOps, SecOps, and Cloud teams to enforce policies and manage servers across hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
What is Puppet?
Puppet is a configuration management and automation tool. It lets you:
- Describe infrastructure as code.
- Automatically enforce configurations on servers.
- Apply updates and security patches consistently.
- Scale from one server to tens of thousands.
Instead of running commands one by one, Puppet makes sure every server matches the state you describe.
Why You Would Use Puppet
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) – treat servers like code, making them versionable and repeatable.
- Compliance and Security – enforce firewall rules, audit settings, and password policies.
- Reduced Human Error – less manual intervention = fewer mistakes.
- Multi-Platform Support – manage Linux, Windows, cloud VMs, and containers.
- Faster Deployments – speed up application rollouts by automating dependencies.
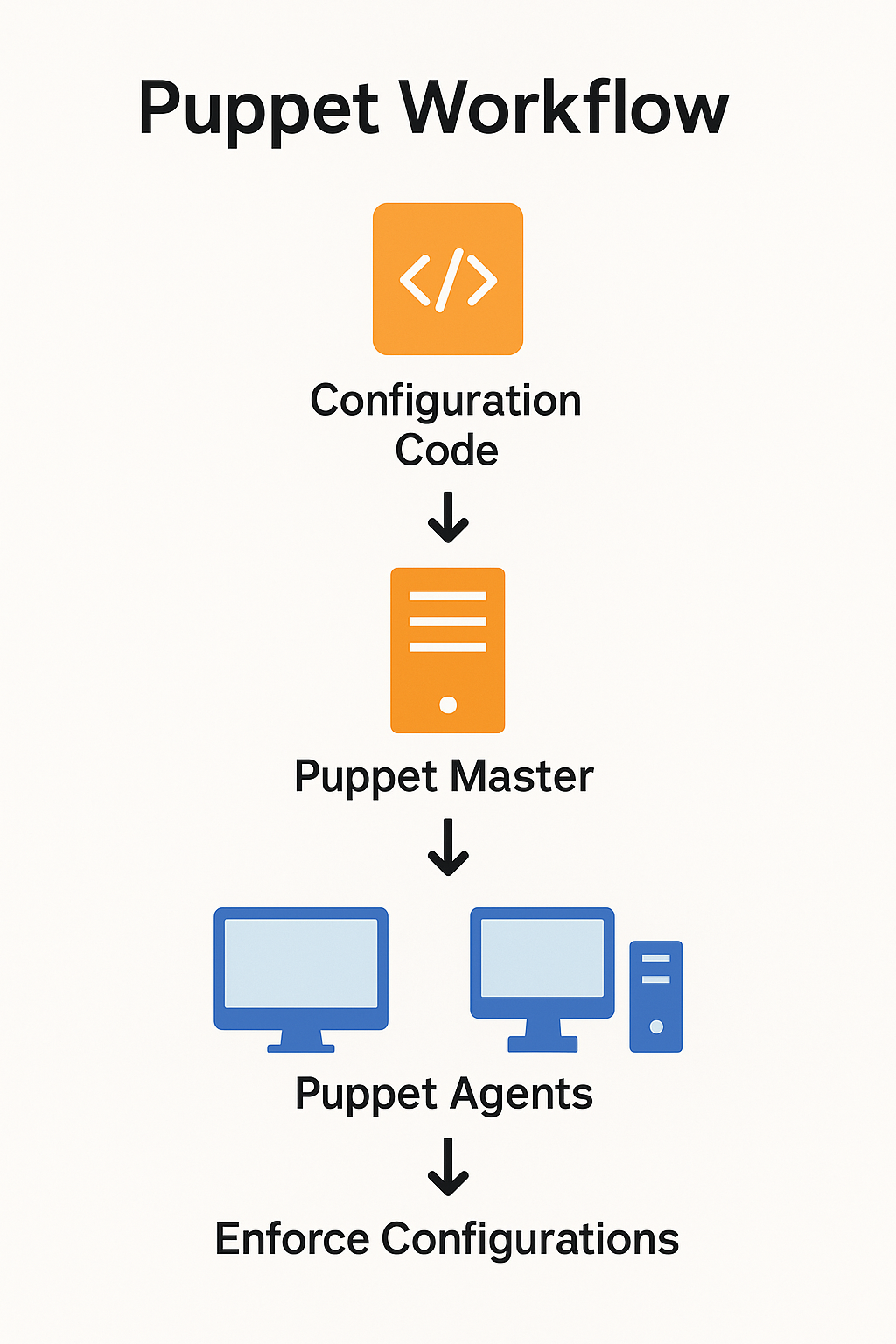
Puppet Architecture Explained
Puppet uses a client-server model.
- Puppet Master (Server): Holds the configuration (catalogs) written in Puppet DSL.
- Puppet Agent (Node): Runs on each server to apply the configuration.
- Communication: Agents request their configuration from the Master over HTTPS.
Diagram: Puppet Master sends configuration catalogs to Puppet Agents across servers.
Writing Puppet Code (Manifests)
Puppet uses its own Domain-Specific Language (DSL), which is human-readable.
Example 1: Installing Nginx
package { 'nginx':
ensure => installed,
}
service { 'nginx':
ensure => running,
enable => true,
require => Package['nginx'],
}
This ensures:
- Nginx is installed.
- The service is enabled and running.
Example 2: Managing a File
file { '/etc/motd':
ensure => file,
content => "Welcome to your Puppet-managed server!",
}
This creates a custom message of the day file.
Advanced Puppet Examples
Deploying a LAMP Stack
package { ['apache2','mysql-server','php']:
ensure => installed,
}
service { 'apache2':
ensure => running,
enable => true,
}
service { 'mysql':
ensure => running,
enable => true,
}
This installs and runs Apache, MySQL, and PHP automatically across all your web servers.
Enforcing Security Policies
file_line { 'password_policy':
path => '/etc/login.defs',
line => 'PASS_MAX_DAYS 90',
match => '^PASS_MAX_DAYS',
}
This ensures passwords must be changed every 90 days.
Real-World Use Cases
- Cloud Deployments – Configure AWS, Azure, and GCP servers at scale.
- Patch Management – Automate security updates for OS and software.
- Enterprise Compliance – Enforce CIS, NIST, or company-specific hardening.
- CI/CD Pipelines – Puppet integrates with Jenkins, GitLab, and other CI/CD tools.
- Disaster Recovery – Rebuild infrastructure quickly from Puppet code.
Puppet vs Other Tools
| Feature | Puppet | Ansible | Chef | SaltStack |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approach | Declarative | Declarative + Imperative | Declarative | Event-driven + Declarative |
| Agentless? | ❌ Requires agent | ✅ Yes | ❌ Requires agent | ✅ Optional |
| Best For | Large enterprises, compliance | Fast start, smaller setups | Complex deployments | Real-time automation |
| Language | Puppet DSL | YAML | Ruby DSL | YAML + Python |
Benefits of Using Puppet
✅ Consistency across environments (Dev, Test, Prod)
✅ Less downtime caused by misconfigurations
✅ Audit trail of every change
✅ Faster onboarding of new systems
✅ Proven tool with a large community and enterprise support
Puppet in Security Operations
For security-focused teams, Puppet can:
- Automatically deploy and manage endpoint agents (CrowdStrike, Taegis, etc.).
- Enforce firewall rules across hundreds of servers.
- Roll out critical CVE patches immediately.
- Maintain golden images for compliance checks.
Getting Started with Puppet
- Install Puppet on a Linux system.
- Define your first manifest.
- Apply it to an agent node.
- Expand into managing packages, services, and files.
- Scale to infrastructure-wide automation.
For beginners, Puppet Bolt (agentless mode) is also available for simpler automation.
Summary
Puppet is a mature, enterprise-grade automation tool that brings order, speed, and consistency to IT operations. Whether you’re managing 10 servers or 10,000, Puppet helps enforce security, deploy applications, and eliminate manual configuration drift.